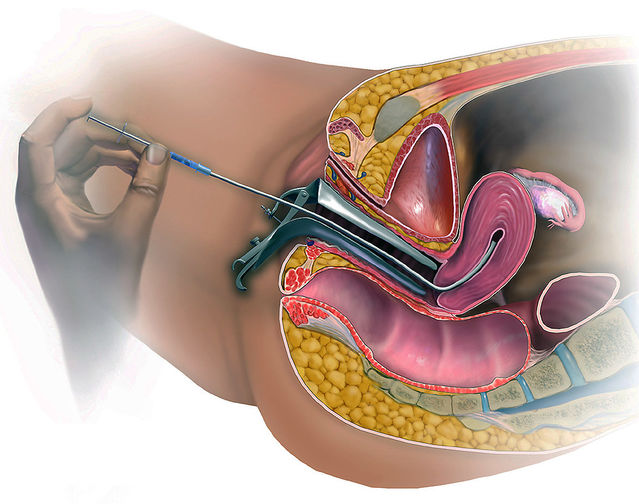
Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is a fertility treatment procedure that involves placing sperm directly into a woman’s uterus to increase the chances of fertilization. IUI is often recommended for couples or individuals with certain fertility issues or in cases where natural conception has been challenging.
Here is a general overview of the IUI process:
- Ovarian Stimulation (optional): In some cases, the woman may be given hormonal medications to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple mature eggs. This step is not always necessary and depends on the specific situation and the recommendation of the fertility specialist.
- Sperm Preparation: The male partner’s sperm or a donor sperm sample is collected and processed in the laboratory. The sperm is washed and concentrated to remove any impurities, non-motile sperm, and seminal fluid. This preparation helps to increase the number of healthy, motile sperm for the insemination process.
- Insemination: The prepared sperm is then inserted into the woman’s uterus using a thin catheter. This procedure is typically performed in the doctor’s office and is generally painless. The timing of the insemination is crucial and is usually done around the time of ovulation, either detected naturally or with the assistance of fertility medications or ovulation induction.
- Rest and Monitoring: After the insemination, the woman may be advised to rest for a short period before resuming normal activities. Subsequent monitoring may involve tracking the woman’s menstrual cycle and, if necessary, additional hormone level measurements or ultrasound scans to assess the development of follicles or the timing of ovulation.
- Pregnancy Testing: About two weeks after the insemination, a pregnancy test is performed to determine if the woman has become pregnant.
IUI is a less invasive and less expensive option compared to in vitro fertilization (IVF). It may be recommended for couples with mild male factor infertility, unexplained infertility, or certain cervical or ovulatory disorders. It can also be used in cases where donor sperm is required or when fertility preservation is desired before medical treatments that may affect fertility.
Success rates of IUI can vary depending on factors such as the woman’s age, the quality of the sperm, the cause of infertility, and the overall health of the couple. It’s important to consult with a fertility specialist or reproductive endocrinologist to evaluate individual fertility concerns, determine the suitability of IUI, and understand the potential success rates and risks associated with the procedure.