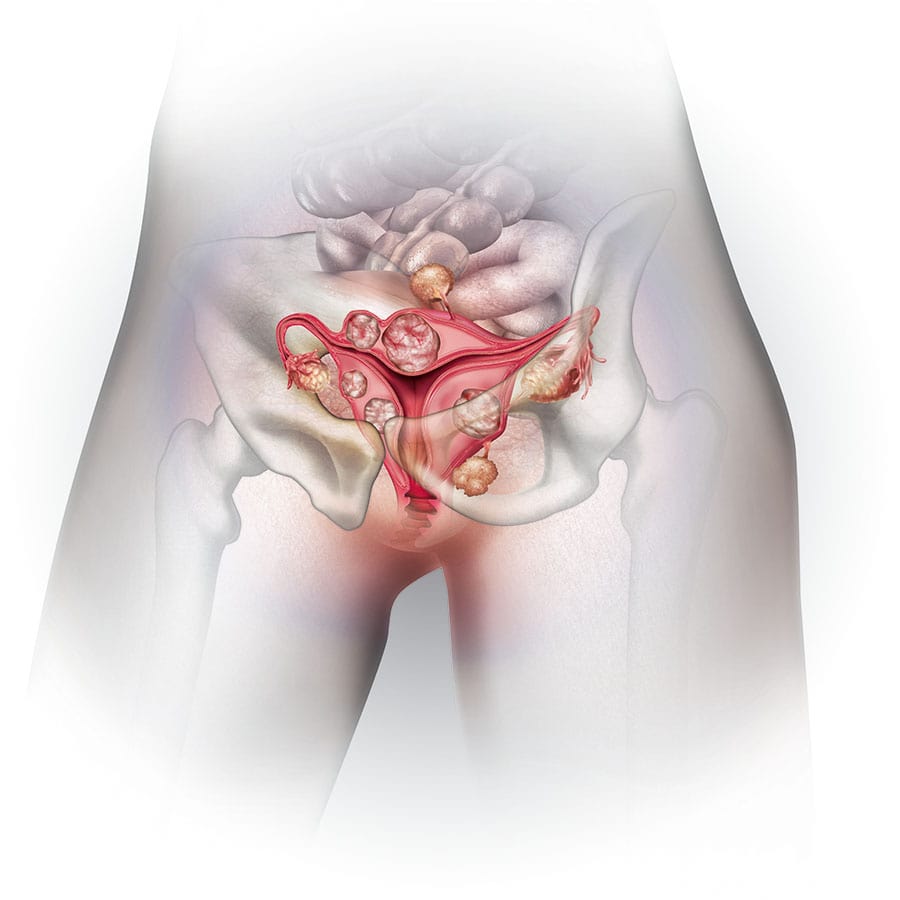
Gynecology encompasses various conditions and disorders that affect the female reproductive system. Two common gynecological conditions are fibroids and endometriosis. Here’s a brief overview of Fibroids (Uterine Fibroids)
- Fibroids (Uterine Fibroids): Fibroids are noncancerous growths that develop in the uterus. They are composed of muscle and fibrous tissue and can vary in size and location. Some women may have one or multiple fibroids. The exact cause of fibroids is unknown, but they are influenced by hormonal factors such as estrogen and progesterone.
Symptoms of fibroids can include:
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual periods
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Frequent urination
- Difficulty emptying the bladder
- Constipation or bloating
- Back or leg pain
- Enlarged abdomen
Treatment for fibroids depends on the severity of symptoms, the size and location of the fibroids, and the individual’s reproductive plans. Treatment options include:
- Medications: Certain medications can help manage symptoms by regulating the menstrual cycle, reducing pain, or shrinking the fibroids.
- Minimally invasive procedures: Techniques such as uterine artery embolization, myomectomy (surgical removal of fibroids), or focused ultrasound surgery may be used to treat fibroids while preserving the uterus.
- Hysterectomy: In severe cases or when fertility is not a concern, the removal of the uterus may be recommended.
It’s important for individuals experiencing symptoms of fibroids or endometriosis to consult with a gynecologist. They can evaluate the symptoms, perform appropriate tests or imaging, and recommend an individualized treatment plan based on the specific circumstances and goals of the patient.