Best PCOS Treatment in Kolkata and Howrah
Looking for the best PCOS treatment in Kolkata and Howrah? Renowned Dr. Anshu Agrawal (Obstetrician & Gynecologist) in these cities offer comprehensive care for managing Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. From hormonal therapy to fertility solutions, expert gynecologists and endocrinologists provide personalized treatment plans. Facilities like ILS Hospital, Belle Vue Clinic, and specialized PCOS care centers focus on lifestyle management, weight control, and advanced therapies to help women lead healthier lives. Consult the best doctors today for effective PCOS management.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is an endocrine disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is a complex condition that involves hormonal imbalances, reproductive issues, and metabolic disturbances. PCOS is one of the most common endocrine disorders among women, and its exact cause is not yet fully understood.
The primary features of PCOS include:
- Irregular periods: Women with PCOS often experience irregular menstrual cycles, characterized by infrequent or prolonged periods, or sometimes the absence of menstruation altogether.
- Hyperandrogenism: Elevated levels of androgens, such as testosterone, are commonly found in women with PCOS. This can lead to symptoms such as excess hair growth (hirsutism), acne, and male-pattern baldness.
- Polycystic ovaries: On ultrasound examination, the ovaries of women with PCOS typically appear enlarged and contain multiple small cysts. However, not all women with PCOS have polycystic ovaries, and the presence of cysts alone is not sufficient for a diagnosis.
In addition to these primary features, women with PCOS may also experience other symptoms and complications, including:
- Insulin resistance: Many women with PCOS have insulin resistance, meaning their body cells are less responsive to the action of insulin. This can lead to high insulin levels in the blood, which may contribute to weight gain and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Weight gain: PCOS is often associated with weight gain or difficulty in losing weight. Obesity and PCOS can aggravate each other, creating a vicious cycle.
- Fertility issues: PCOS is a leading cause of infertility in women. Irregular ovulation or the lack of ovulation can make it challenging to conceive.
- Metabolic syndrome: Women with PCOS have an increased risk of developing metabolic syndrome, which includes high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
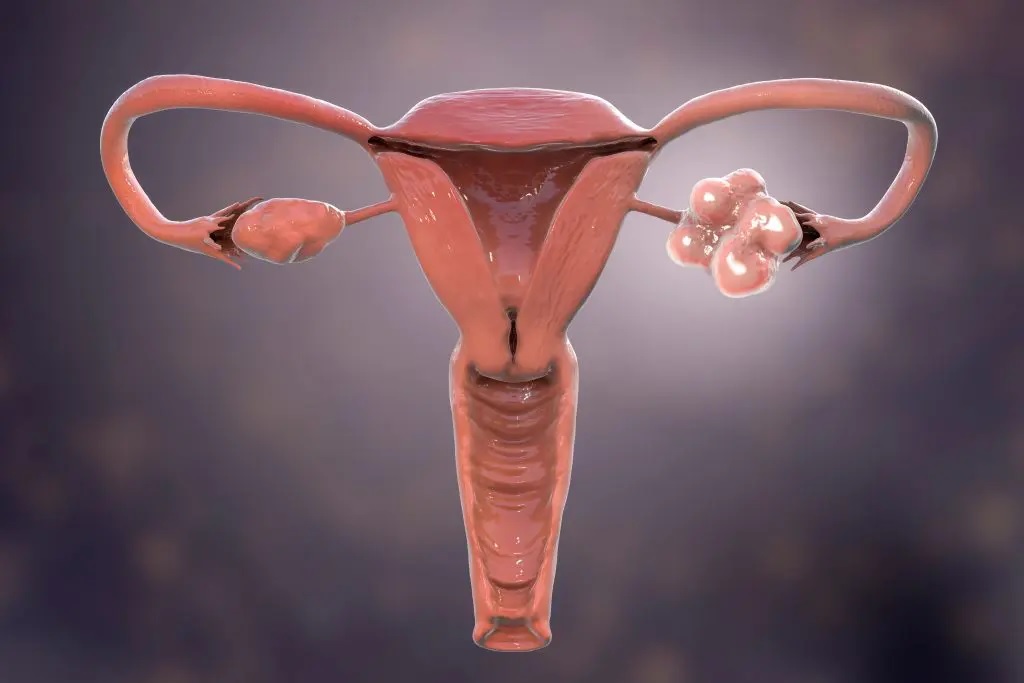
The diagnosis of PCOS is usually based on the presence of specific signs and symptoms, including irregular periods, hyperandrogenism, and polycystic ovaries on ultrasound. Other possible causes of the symptoms should be ruled out as part of the diagnostic process.
Management of PCOS typically involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight through exercise and a balanced diet, as well as medical interventions. Treatment options depend on the individual’s goals and may include hormonal contraceptives to regulate the menstrual cycle, medications to manage insulin resistance and lower androgen levels, and fertility treatments for those trying to conceive.
It’s important for women with for best PCOS treatment in Kolkata and Howrah to work closely with healthcare providers who specialize in reproductive endocrinology or gynecology to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and goals. Regular monitoring and ongoing management are essential to minimize symptoms, reduce the risk of long-term complications, and optimize overall health

